How to Create Dynamic Forms in Angular Using a Dictionary Interface
Creating dynamic forms in Angular can be a powerful way to handle flexible data structures, especially when working with APIs that return complex or nested JSON objects. In this article, I will show you how to create dynamic forms in Angular using a Dictionary interface and a dynamic form generator service.
Defining the Dictionary Interface
First, let’s define the Dictionary interface. This interface allows us to have a recursive type that can contain either strings or nested dictionaries:
1
2
3
export interface Dictionary {
[key: string]: string | Dictionary;
}
Creating the Dynamic Form Generator Service
Next, we need a service that can create form controls based on the structure of the dictionary. This service will recursively create form groups for nested dictionaries and form controls for string values.
Here is the DynamicFormGeneratorService:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class DynamicFormGeneratorService {
#fb = inject(FormBuilder);
createForm(data: Dictionary): FormGroup {
const formControls = this.createControls(data);
return this.#fb.group(formControls);
}
private createControls(data: Dictionary): { [key: string]: AbstractControl } {
return Object.keys(data).reduce((controls, key) => {
if (typeof data[key] === 'object' && data[key] !== null) {
controls[key] = this.#fb.group(this.createControls(data[key] as Dictionary));
} else {
controls[key] = new FormControl(data[key] as string, Validators.required);
}
return controls;
}, {} as { [key: string]: AbstractControl });
}
}
Creating the Dynamic Form Group Component
Now, let’s create a component that will use this service to generate a form based on the dictionary data. This component will be responsible for rendering the form and handling form submissions.
Here’s the TypeScript for the DynamicFormGroupComponent:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
@Component({
selector: 'app-dynamic-form-group',
standalone: true,
imports: [ReactiveFormsModule],
templateUrl: './dynamic-form-group.component.html',
})
export class DynamicFormGroupComponent implements OnInit {
@Output() formValues = new EventEmitter<Dictionary>();
@Input() initialData?: Dictionary;
@Input() formGroup: FormGroup = new FormGroup({});
#dynamicFormService = inject(DynamicFormGeneratorService);
objectKeys = Object.keys;
ngOnInit(): void {
if (this.initialData) {
this.formGroup = this.#dynamicFormService.createForm(this.initialData);
}
}
onSubmit(): void {
if (!this.initialData || this.formGroup.invalid) return;
this.formValues.emit(this.formGroup.value);
}
isGroup(control: AbstractControl | null): control is FormGroup {
return control instanceof FormGroup;
}
getFormGroup(control: AbstractControl | null): FormGroup {
return control as FormGroup;
}
}
And the corresponding HTML template:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
<form
[formGroup]="formGroup"
class="p-6 bg-indigo-50 border border-red-200 rounded-lg shadow-sm space-y-4"
>
<!-- This loop iterates over the keys of the formGroup.controls object. -->
<!-- Each key represents a form control or a nested form group. -->
<ng-container *ngFor="let key of objectKeys(formGroup.controls)">
<!-- This condition checks if the current form control is a FormGroup. -->
<ng-container *ngIf="isGroup(formGroup.get(key)); else singleControl">
<!-- If it is a FormGroup, a fieldset is created for it. -->
<fieldset
[formGroupName]="key"
class="border border-gray-300 rounded-lg p-4 bg-white"
>
<legend class="text-lg font-semibold text-gray-700 mb-2"></legend>
<!-- The nested FormGroup is passed to the component using the formGroup input property. -->
<app-dynamic-form-group
[formGroup]="getFormGroup(formGroup.get(key))"
></app-dynamic-form-group>
</fieldset>
</ng-container>
<ng-template #singleControl>
<!-- If the current form control is not a FormGroup, an input field is created for it. -->
<!-- The formControlName directive associates this input field with the form control. -->
<div class="flex flex-col space-y-2">
<label [for]="key" class="text-sm font-medium text-gray-600"></label>
<input
[formControlName]="key"
id=""
class="p-2 border border-gray-300 rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-indigo-500"
/>
</div>
</ng-template>
</ng-container>
<!-- This condition checks if initialData is available and adds a submit button if it is. -->
<button
*ngIf="initialData"
(click)="onSubmit()"
[disabled]="formGroup.invalid"
class="bg-indigo-500 text-white px-4 py-2 rounded-lg hover:bg-indigo-600 disabled:opacity-50 disabled:cursor-not-allowed"
>
Submit
</button>
</form>
Putting It All Together
To use this dynamic form in your application, you would typically have a parent component that provides the dictionary data and handles the form submission:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
export class AppComponent {
title = 'dynamic-forms';
onFormValues(values: Dictionary) {
console.table(values);
}
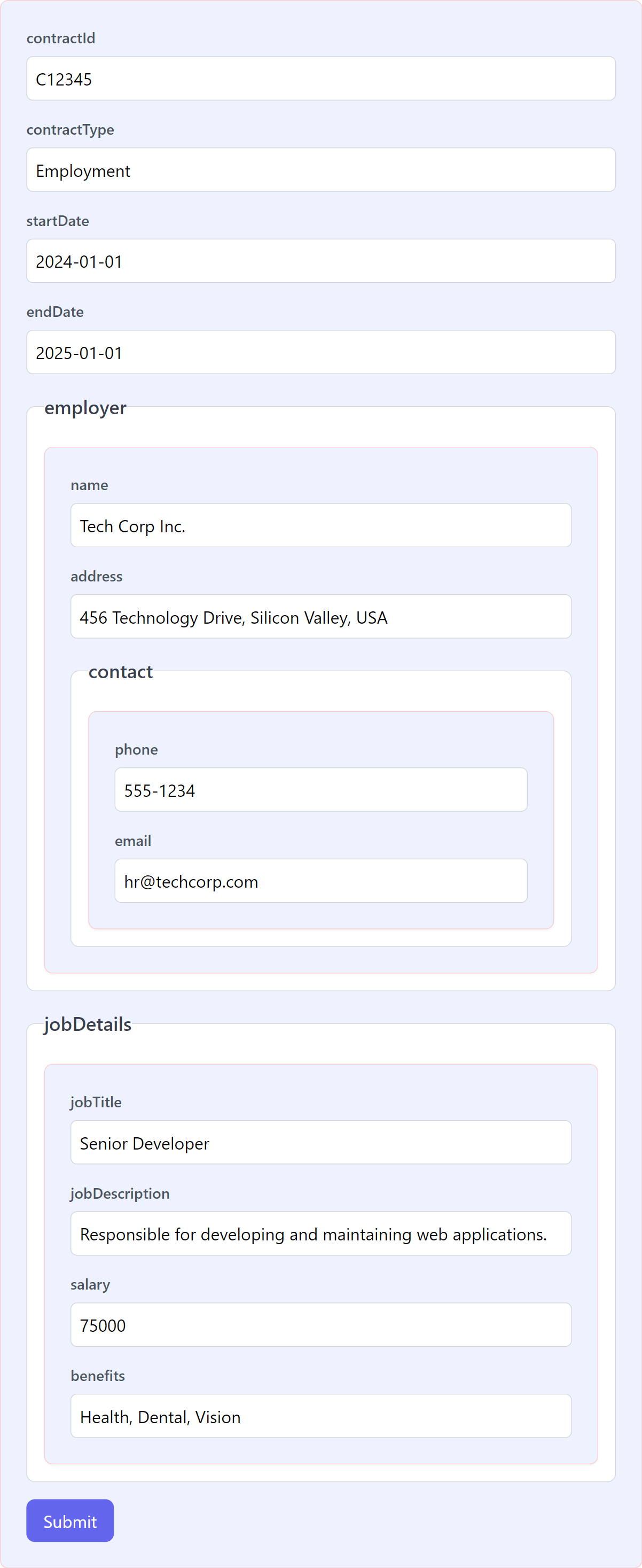
contract: Dictionary = {
contractId: 'C12345',
contractType: 'Employment',
startDate: '2024-01-01',
endDate: '2025-01-01',
employer: {
name: 'Tech Corp Inc.',
address: '456 Technology Drive, Silicon Valley, USA',
contact: {
phone: '555-1234',
email: 'hr@techcorp.com',
},
},
jobDetails: {
jobTitle: 'Senior Developer',
jobDescription:
'Responsible for developing and maintaining web applications.',
salary: '75000',
benefits: 'Health, Dental, Vision',
},
};
}
Preview
Conclusion
In this article, we have demonstrated how to create a dynamic form in Angular using a dictionary interface. By leveraging Angular’s reactive forms and a recursive approach, you can generate complex forms that adapt to any data structure. This method is particularly useful for handling dynamic data from APIs and creating flexible form components.